In the large-scale population cohort epidemiological investigation, the changes of biological sample detection indicators can quickly and truly reflect the changes of physiological indicators and pathological state of the body, and play an irreplaceable role in studying the relationship between life outcomes and exposure factors, and exploring the risk factors and pathogenesis of diseases and other outcomes. The types of biological samples collected in cohort study mainly include tissues, cells and body fluids, etc. By detecting these biological samples, researchers can study the effects of gene and environmental changes on the body from multiple molecular levels such as nucleic acid, protein, endogenous metabolic small molecular substances, environmental chemicals and their metabolites. With the development of omics technology, it can provide strong evidence for clarifying the relationship between environmental exposure and outcome, revealing the pathogenesis of diseases, and formulating disease prevention and control strategies by using large population biological samples to study genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, exposure omics, etc.
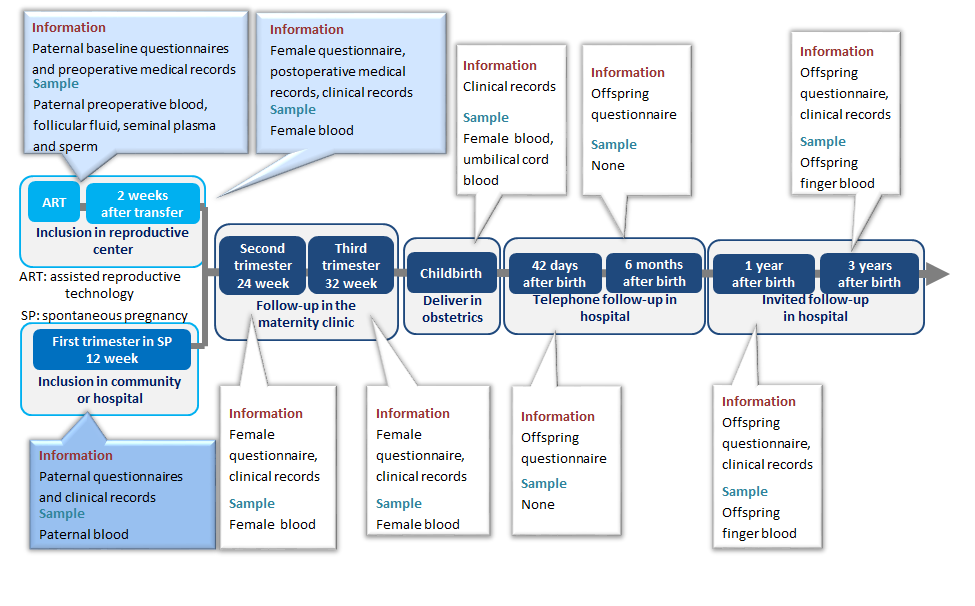
The collection of birth cohort samples is mainly carried out in hospital laboratory or obstetrics department, and is included in the whole cohort. The types of samples collected during the follow-up process include blood, follicular fluid, semen and urine of couples receiving ART treatment, as well as maternal blood, cord blood and offspring blood after successful conception; Blood of pregnant women and their spouses in natural pregnancy, urine of pregnant women and their spouses, cord blood and offspring blood.
Sample Species
1. Blood
(1) Anticoagulant adult venous blood,separated into plasma and blood cells, can be derived into DNA, RNA and protein.
(2) Anticoagulant cord blood, separated into plasma and blood cells, can be derived into DNA, RNA and protein.
(3) Anticoagulant peripheral blood of children, separated into plasma and blood cells, can be derived into DNA, RNA and protein, etc.
2. Urine
3. Follicular fluid
4. Semen, separated into seminal plasma and sperm.
5. Placenta.
6. The endometrium.
7. Meconium.
8. Umbilical cord blood